Summary. Circulating on the Internet and elsewhere is the erroneous claim that every barcode in the Universal Product Code (UPC-A) has the number 666 embedded in it. A look at how the numbers in the UPC barcode are constructed will show why this claim is wrong.
How the error may have occurred. Someone glancing casually and a bit carelessly at a UPC barcode containing the number six will note that there are two thin vertical bars almost directly above the number six. Here, for example, is the barcode from a box of After Eight dinner mints. Note the two thin bars above the six in the 48600:
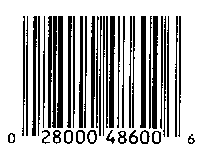
Reading between the lines. By looking more carefully at a barcode, you can see that not only are the bars of different widths, but the spaces between the bars vary also. This is the key: each number in the barcode is represented not by two lines, but by four elements, which include two lines and two spaces. Further, if you look even more closely, you will see that for a given number (such as a six), what is a line on the right side of the barcode is a space on the left side and what is a space on the right side of the barcode is a line on the left side. (The different representations allow the barcode scanner to differentiate between the manufacturer’s number and the item number even if the barcode is scanned upside down or sideways.) Here, for example, is the barcode from a Master Locks combination padlock:
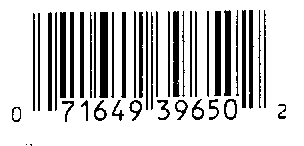
To make this even plainer, here is a barcode containing all sixes:

Guarding the edge. The lines at each end of the barcode are guard bars, consisting of a thin line, a thin space, and a thin line. Since there are only three elements instead of four, no number of any kind is represented. (No very wide space or very wide bar is there to complete the number six, for example.)
And the middle. In between the first five numbers (which represent the manufacturer’s identifying number–who made the product) and the last five numbers (which represent the specific product code–such as a blue, medium ball-point pen) is another set of guard bars, consisting of a thin space, a thin line, a thin space, a thin line, and a thin space. Here, even though there are five elements (two bars and three spaces), they do not represent a number because none of the numbers are made up of all thin elements (see below).
Breaking the code. Since the lines and spaces appear in four different widths, we could use the words thin, medium, wide, and very wide to represent them. We can also use numbers, though, with 1 representing thin, 2 representing medium, 3 representing wide, and 4 representing very wide. That plan allows us to represent each number this way:
- 0 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 3-2-1-1
- 1 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 2-2-2-1
- 2 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 2-1-2-2
- 3 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-4-1-1
- 4 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-1-3-2
- 5 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-2-3-1
- 6 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-1-1-4
- 7 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-3-1-2
- 8 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 1-2-1-3
- 9 is formed by alternating bars and spaces of width 3-1-1-2
- An end guard bar is formed by two bars and a space 1-1-1
- A middle guard bar is formed by two bars and three spaces 1-1-1-1-1
Putting it all together. Let’s return to the padlock barcode, enlarged and detailed here. Note that the barcode contains two sixes, one on each side of the middle guard bars. As mentioned above, you can see the difference in representation of the same 1-1-1-4 code for a left-hand six, where the very wide segment is a bar instead of a space, and the right hand six, where the very wide segment is a space rather than a bar. Yet you are looking at the same number.

Further Issues About the Mark of the Beast, 666, Barcodes, and the Bible
Since the only information we have about the Mark of the Beast and the number 666 comes from the Bible, we should look at the Bible to see the context of these things. The Mark of the Beast is discussed in Revelation 13 and 14.
Who is the Beast? The Mark is ordered to be put on people by the False Prophet (the “second beast”), who serves the Antichrist (the “first beast”). The False Prophet is evidently a human being, not a system of commerce. So, who is this person? Before we say that barcodes are the Mark of the Beast, we should identify the Beast whose mark they supposedly are.
Are we in the Great Tribulation? The Mark of the Beast is not put on people until a little past halfway through the Great Tribulation, that is, more than three and a half years into the tribulation. Are we in such a tribulation now? In the first half of the tribulation, a third of mankind will be killed. Did this happen?
Did the World End? From the time of the Mark of the Beast until Armageddon, which pretty much ends the world, less than three and a half years pass. The UPC barcode has been around for twenty years.
Pre- Mid- or Post-trib? Of the three schools of interpretation for Revelation end times, pretribulationists and midtribulationists both believe that the church will be raptured before the beast and the false prophet arrive and put their mark on people. Only posttribulationists believe that Christians will be around during marking time. Thus, is you believe that the UPC barcode is the mark of the beast, you are a posttribulationist. Since most of the evangelical world is pretribulationist, what evidence do you provide to argue that you are correct and most other interpreters are wrong?
It’s on You. The Mark of the Beast is clearly described as being either on the forehead or on the hand, not on commercial products. Explain this discrepancy.
Can we pick and choose the numbers? The Mark of the Beast is 666, but this barcode I’m looking at is 045342987531. If the guide bars are really sixes, then the number I’m looking at is 604534269875316. How is that the same as 666 any more than 16066 Jones Street is the same as 666? Just because we can pick three sixes out of a string of numbers, we cannot really say that those are the same as the single number 666.
Why the UPC and not another bar code? There are many barcode symbologies. In fact, the UPC may be on the way out, to be replaced by newer, more informatoin rich schemes such as the EPC. In the meantime, why should the UPC be singled out? Here are some of the other common barcodes:
2 of 5
3 of 9
Australia Post
Codabar
Code 11
Code 39 and extended (full ASCII) Code 39
Code 93
Code 128
Code B
Deutschen Post
EAN 8*
EAN13*
EAN 128
ISBN
ISSN
ITF-14
ITF-6
Interleaved 2 of 5
JAN*
Matrix 2 of 5
MSI (Modified Plessy)
Plessey
PostNet & FIM
Royal Mail 4 State
Swiss Post
Telepen (numeric and ASCII).
UPC-A*
UPC-E*
(* including 2 and 5 digit supplementaries)
For further reading:
http://www.barcodeisland.com/symbolgy.phtml
How UPC Barcodes Work
Barcode Server
Uniform Code Council ID Numbers and Bar Codes
Bar Codes (See how the lines and spaces represent seven-digit binary coded numbers.)